Gimmick-free technology that is always advancing and always learning.

Gimmick-free technology that is always advancing and always learning.

Step 1 : Molecular Design
Select mode of molecular assembly
Required degree and type of cure-functionality for chemical and physical properties and co-polymerisation dynamics
Functional side groups for compatibility and adhesion
Component blocks for desired physical properties
End groups for synthesis reactivity and/or product characteristics such as adhesion and compatibility
Step 2 : Synthesis
Small scale laboratory synthesis
Initial reaction profile and progress including inter-step evaluation fo reaction progress
Preliminary reactivity test of candidate oligomer
Preliminary evaluation of physical and rheological properties
Drop-in candidate molecule into test formulation for screening test
Move to small batch pilot synthesis of molecules that show desired potential and performance

Step 3 : Molecular Characterisation
Stability during synthesis
Post-synthesis stability under variable temperature conditions
Colour and colour stability
Viscosity and Molecular weight distribution
Refractive index
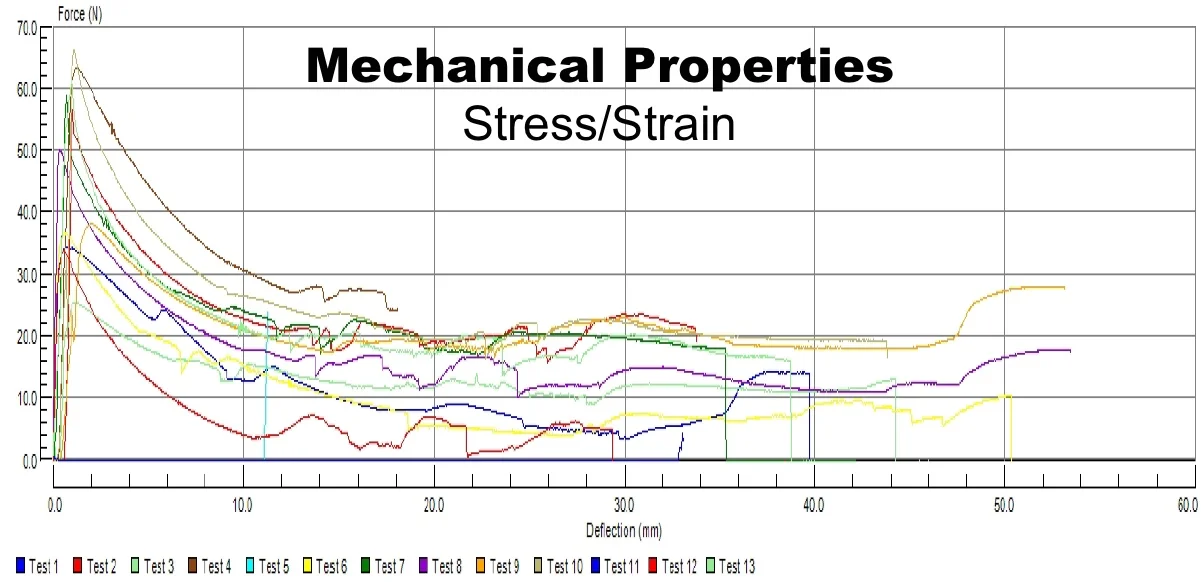
Mechanical Properties; including Tensile Strength, Elongation, Flexural strength and displacement, Elastic and Plastic deformation and Yield Stress.
Secondary Mechanical properties such as Scratch Resistance, Marring Resistance, Impact resistance
Chemical properties such as Glass-Point transition, water absorption, chemical and solvent resistance, stain resistance
Colour and performance stability under accelerated Ultra-Violet ageing